A crypto wallet is a software program that allows a user to store either fiat money or cryptocurrencies online.
A crypto wallet, also known as a software or digital wallet, is a software program that allows a user to store either fiat money or cryptocurrencies online.
A cryptocurrency wallet, also known as a software or digital wallet, stores the user’s private keys (wallet passwords) securely and is accessible. This allows the user to access and transact their digital, blockchain-based assets easily, which is why people usually refer to wallets as storing their cryptocurrency. Assets stored in the crypto wallet can be used for transactions such as purchases. Crypto wallets can also store passwords and track user transaction history. Crypto wallets for cryptocurrencies facilitate direct peer-to-peer payments without the assistance of intermediaries.
How does a crypto wallet work?
Crypto wallets store the user’s private key to their blockchain address. This address contains their cryptocurrency. Assets stored in the crypto wallet can be used for transactions such as purchases, decentralized finance (DeFi) purposes, and token swapping. Crypto wallets can also track user transaction history. Some crypto wallets also facilitate direct peer-to-peer payments, without the assistance of intermediary dApps.
Popular cryptocurrency wallets
To give you an idea about what you can expect from various wallets, we will provide some brief overviews of a few self-custody crypto wallets below:
MetaMask

MetaMask is a popular basic cryptocurrency wallet that is designed exclusively for Ethereum-based altcoins and NFTs. It is usually listed as a suggested wallet for DeFi and gaming dApp platforms when you sign up with a platform due to its ease of use.
However, with MetaMask it is only possible to store and purchase cryptocurrency; it offers no additional services such as token swapping.
Since there are many blockchain platforms built on top of the Ethereum blockchain, it is compatible with thousands of tokens, including those of dApps built on the Polygon blockchain.
Phantom

Phantom is a single-chain wallet designed for compatibility with Solana-based tokens and NFTs. Although it was only released in 2021, it rapidly gained popularity due to its being one of the few exclusive Solana wallets and the fact that the coding was audited by Kudelski Security.
Another major feature is its emphasis on security, as it focuses on identifying and preventing malicious attacks against its users, such as phishing attacks and spam NFTs by alerting users to possible attacks before the transaction is complete.
An additional feature that they have is a bug bounty that rewards users with up to $50,000 rewards if they can identify any vulnerabilities that may put users’ funds at risk.
Trust Wallet

Trust Wallet is a multi-chain wallet that has been downloaded over 25 million times. It allows users to store and transact over 4.5 million different digital assets and offers live price indexes of altcoins stored in your wallet thanks to its integration with various partnered payment networks and cryptocurrency exchange platforms, as well as enabling token swapping and staking of 12 cryptocurrencies.
Trust Wallet also offers an in-app cryptocurrency exchange platform for mobile devices so that you do not need to connect it to any third-party apps.
BitKeep

BitKeep is a multichain wallet that enables users to import their existing wallets to their BitKeep wallet, thereby allowing them to manage their cryptocurrency portfolio from a single wallet.
BitKeep also provides real-time prices for compatible cryptocurrencies, which can then be purchased, sold, or swapped directly through the wallet, as well as an in-app NFT marketplace.
It is considered to be a beginner-friendly multi-chain wallet.
How to create a crypto wallet
Creating a wallet usually entails variations of the following steps:
- Go to the Wallet Download page on the official website and then download the relevant wallet app
- Open the app and grant permission to the App
- Select Get Started on the home screen
- Select Create a new wallet
- Set your password
- Write down your 12/24-word Secret Recovery Phrase and save it somewhere safe
- Confirm your Secret Recovery Phrase
The user first needs to register for a crypto wallet. Creating a wallet on a cryptocurrency exchange platform or other third-party payment platforms may involve more steps.
The extent of the KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements is dependent on the country in which it is based and the country in which you are trading. For instance, PayPal requires its users to enter their bank account and credit card details when registering for a PayPal account. PayPal will then use this data to perform KYC verification checks.
Similarly, in the past, it wasn’t necessary for cryptocurrency exchange platform users to register their personal information on the website to perform transactions. However, with the increasingly tight regulations being applied to the cryptocurrency space in reaction to the high levels of fraud, money laundering, and theft occurring in the industry, cryptocurrency exchange platforms now need to be more careful about whom they allow to transact on their platforms and to more carefully monitor these transactions as well. Stand-alone cryptocurrency wallets, on the other hand, don’t necessarily usually require KYC. MyEtherWallet is a notable example.
Types of crypto wallets
To understand which crypto wallet is the right one for you, it is helpful to understand which kinds of crypto wallets there are. To start with, there are two broad types of crypto wallets, namely hot and cold wallets.
- Hot wallets, also known as software wallets, refer to wallets that are stored online.
- Cold wallets are used to store digital assets offline.
Within these two broad categories, there are several different types of wallets.
Desktop wallets
Desktop wallets are a type of hot wallet that is installed directly onto your personal computer and is stored on your hard drive. They are usually compatible with browsers and can be added as a browser extension.
Common examples of desktop wallets include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and the Coinbase Wallet.
These wallets are usually non-custodial, meaning that only you have control of your digital assets and private keys.
Some desktop wallets offer additional services such as token swapping, staking, and purchasing cryptocurrency directly through the wallet itself.
Web wallets
Web wallets are crypto wallets that are offered through third-party platforms such as cryptocurrency exchanges. This means that your wallet’s private keys are stored on their platform, which is why they are typically custodial wallets.
‘Custodial’ means that another party has control of your assets and private keys, even if the contents are password protected. Therefore, if the security of the platform is compromised, or the platform goes bankrupt, your digital assets will be at risk.
Mobile wallets
A mobile wallet is a software wallet that is downloaded and installed onto your smartphone, thereby allowing you to use it to store and trade cryptocurrencies on your device.
Many desktop wallets have mobile versions, which will allow you to access your crypto from both platforms. This is preferable to mobile-exclusive apps since it will be difficult to regain access to your wallet if you lose your device.
Other concerns to be aware of are fake versions on app stores that trick you into installing malware. This is why it is best to follow the mobile links from the official websites than to try searching for the wallet on an app store.
Like desktop wallets, some mobile wallets also offer a wider array of services beyond simply storing private keys.
Hardware wallets
Hardware wallets are a type of cold storage wallet that enables you to store your private keys and addresses on a hardware device that is like a USB.
Popular examples of hardware wallets include Trezor and Ledger wallets.
As with a software wallet, it too is password protected. The strength of a hardware wallet is that it cannot be hacked unless it is plugged into a device. The downside is that since it is not stored on the web, there is no seed recovery phase, so if you lose it, your crypto is also lost.
Paper wallets
Paper wallets also allow users to store their private keys offline. It does so by encrypting both the wallet address and wallet private key as a QR code that is printed on a piece of paper.
You might want to consider laminating it to ensure that it doesn’t get damaged before storing it somewhere safe and inaccessible to others.
Paper wallets are even more secure than hardware wallets since they can only be used when scanned. However, that also makes using it a lot more fidgety.
What is a crypto wallet address?
A wallet address is a location where your cryptocurrency’s private keys are stored. A private key is an encrypted key that is used to show ownership of a wallet address.
These keys give access to the cryptocurrency that they represent on a particular blockchain by creating a digital signature without actually revealing the private key itself.
Private keys are represented as a unique string of randomly generated characters instead of a recognizable word or phrase. A private key is a 256-bit number, meaning that it comprises a 256-digit-long combination of 0s and 1s.
The private key indicates ownership, so only the private key holder can send digital assets from the associated wallet address.
The address, on the other hand, is publicly known, so anyone can send crypto to it.
Wallet addresses usually comprise between 26 to 35 alphanumeric characters, depending on the blockchain.
The addresses of different blockchains are distinguishable from one another, as well. For instance:
- Bitcoin addresses start with either ‘1,’ ‘3’ or ‘bc1’
- Ethereum addresses begin with ‘0x’
- Dogecoin addresses start with a ‘D,’ followed by a digit or capital letter
- Litecoin addresses always begin with either an ‘L’ or an ‘M’
- Ripple addresses always start with an ‘r’
Where can I find my wallet address?
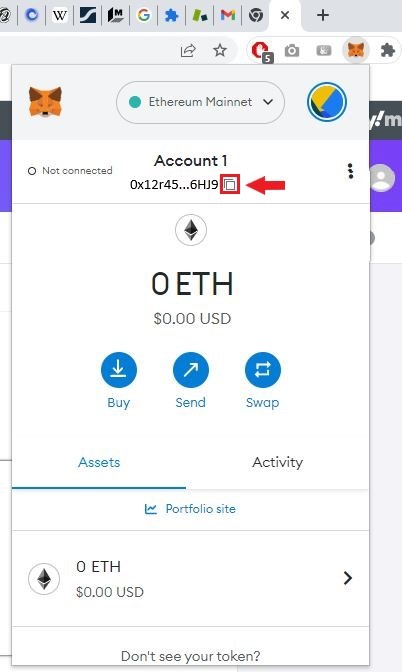
For a single-chain wallet, which only supports one type of blockchain, its wallet address can usually be found at the top of the wallet. This can either be copied or scanned with the QR code. Here is an example from MetaMask, one of the most popular Ethereum crypto wallets:
Centralized vs. decentralized wallets
Counter-intuitively, not all blockchain-based wallets are decentralized. A ‘centralized’ wallet is a custodial crypto wallet, meaning that it is controlled by a third party rather than the owner. A common example of this is an on-platform wallet for cryptocurrency exchanges and DeFi apps. This means that the private keys, and therefore the digital assets within the wallet are not under the owner’s control, but under the custodian’s as they are responsible for safeguarding the contents on the owner’s behalf. The benefit of doing this is that it makes trading on the platform easier. The downside is that if their system is hacked your private keys are at risk, and if the platform goes bankrupt, then your assets are frozen and possibly lost to you, among other concerns.
On the other hand, decentralized wallets are not connected to any third-party website. Therefore, the private keys and wallet contents are completely under the owner’s control. Most desktop wallets are non-custodial. The weakness is that you are responsible for the due diligence of anyone with whom you want to transact and to verify the authenticity of proposed smart contracts on your own.
Why should I use a crypto wallet?
Firstly, it is impossible to own or transact cryptocurrency without a wallet address. Secondly, as stated previously, decentralized cryptocurrency wallets are crypto wallets are usually encrypted, thereby making the contents inaccessible without the correct private key. All transactions are transparent, traceable, and locked into the blockchain, thereby preventing double-spending, data corruption, and tampering.
Furthermore, the necessity of a private key wallet address to access the crypto wallet’s content and perform transactions also decreases the chance of hacks, especially as the wallet address is extremely long and therefore difficult for hacking software to correctly guess, a private key is usually very complex. The user also doesn’t need to provide proof of identity beyond providing their crypto wallet’s address to other parties with whom they would like to conduct a transaction. It is necessary to own a blockchain crypto wallet if the user wants to own or transact cryptocurrencies and tokens, as they are all based on the blockchain.
How to protect your crypto wallet
Aside from the obvious measures the most important rule is to not share your password or secret security phrase private keys with anyone else ever, some hardware crypto wallets can be used to store their assets offline, when not immediately needed, such as Trezor. Another alternative is the paper wallet. This allows a user to print out their private and public keys for offline storage. It is probably advisable to laminate this, as if it were to be destroyed, it would render it completely impossible for their assets to be retrieved. It is also advisable to keep both wipes of wallets in an extremely safe place to avoid theft and to scrape the memory on the printer to eliminate any kind of digital copy there might be of the paper wallet.
It is also a good idea to spread out your digital assets across several wallets so that if one wallet is somehow compromised you won’t lose everything. So too, when you are planning on trading through a cryptocurrency exchange platform, only store the crypto or NFTs that you would like to trade or stake on that wallet. The rest should be kept elsewhere.
Crypto wallet terminology
- Private key: A blockchain or private key is the blockchain version of a password.
- Cryptocurrency exchange: A cryptocurrency exchange is an online platform that allows its users to trade fiat currencies for cryptocurrencies and to exchange cryptocurrencies for other cryptocurrencies and tokens.
- Decentralized: Decentralization is when the decision-making processes and activities of an organization are distributed across various locations instead of just being conducted in a single, central location.
- Fiat currency: Fiat currency is the legal tender that is issued by a government, person, or institution and given value by them without having any resources to back them up.
- Gas fee: The gas fee is the unit price of processing power required to perform a transaction on the blockchain.
- Minting: Minting refers to the creation of new cryptocurrencies or NFTs through a proof-of-stake consensus protocol.
- Wallet address: A blockchain address, or ‘crypto address,’ is something like a cryptographic email address that is unique to the address holder.
Crypto wallet FAQ
Do crypto wallets work in all countries?
Most crypto wallets will work in most countries, except for countries and territories that are largely those that are sanctioned according to any trade embargoes, UN Security Council Resolutions (“UNSCR”), or HM Treasury’s financial sanctions regime.
Can I store all my cryptocurrencies in one wallet?
If you have a multichain wallet such as Exodus or Trust wallet, then yes. But if you have a single-chain wallet like MetaMask (Ethereum only) or Phantom (Solana only), then no.
Can I buy and trade cryptocurrency directly within my wallet?
It depends on the wallet whether you can buy and trade cryptocurrency directly within your wallet.
Can I add money to a crypto wallet?
Most wallets are not compatible with fiat currencies. Even those that are compatible, such as BitKeep, Coinbase, and Exodus, are only compatible in that they allow you to purchase cryptocurrencies with your credit card in-app and to sell crypto for fiat, with the fiat automatically being deposited into your bank account.
There are also fiat wallets, such as those available on Crypto.com which allow you to store fiat, but they act the same as a regular bank account, without fees. Meaning they are a place to store fiat to buy and sell cryptocurrency outside of the wallet itself, while also allowing you to transfer fiat to and from your bank account. These wallets are compatible with fiat only.
Can a crypto wallet be hacked?
Technically a decentralized wallet cannot be hacked. It is only if the user’s password or secret security phrase is compromised that the hacker can get in. But there are many ways that a scammer can get around this.
Can a crypto wallet be traced?
All inter-wallet transactions can be traced on the blockchain. However, unless the user connects their wallet to a third-party platform that requires KYC, the owner of the address should remain anonymous.
What is the best Ethereum wallet?
MetaMask is one of the best pure Ethereum wallets.
How can I find an old crypto wallet?
The only way to restore an old crypto wallet is with the password and secret security phrase. If you have lost them, then there is nothing that can be done. You can find out more about how this happens here.
What crypto wallet has the lowest fees?
The crypto wallet with the lowest service fees is the Exodus Wallet. Note that gas fees are charged by the blockchain, not the wallet.







