
Technology is all around us and in many instances, it has simplified our daily lives through smartphones, the convenience of modern banking, automated cars as well as industrial automation just to name a few. The energy markets, however have not adapted to the speed of modern technological advancements. Monopolistic control has stifled the competition growth, leaving the big energy suppliers to continue producing inefficient utilities at high costs.
Energy One comes in as the game changer that aims to shake-up the industry by becoming the number one energy supplier combining cost cutting and game changing blockchain technology with uncompromising customer orientation and first-class service.
We explore the top five problems currently facing the sustainable energy movement, giving a better understanding of the necessity and value of utilizing sustainable energy resources, and moving toward a cleaner, more cost-effective future.
1. High Energy Costs
Electricity is important to everyday lives. Each year we see an increase in residential, commercial and industrial electricity bills, sometimes far exceeding the inflation rate. In 2017, a study was done in South Africa comparing electricity prices over a ten year period. The study concluded that in a decade, electricity costs rose by 356%, far exceeding the inflation rate, which increased by 74%. Unfortunately this continues to be on an upward rise with no indications of slowing down.
Each country has a unique set of factors contributing to their electricity prices. For example, access to fossil fuels may be limited, meaning the price of fuels will incur additional transportation costs hiking up the price of electricity, compared to a country that extracts its own fuel. Bitcoin has also faced its own struggles with its environmental impact. The cost of generating electricity is the highest component influencing electricity price, here are several other factors that are relevant across the board when determining electricity costs.
2. Depleting Resources
The rate at which the world consumes fossil fuels is increasing rapidly. As the population increases, the electricity demands go up, factoring in parts of the world that are moving into more developed states demanding more energy. Below is a graph showing future energy reserves for coal, gas and oil:
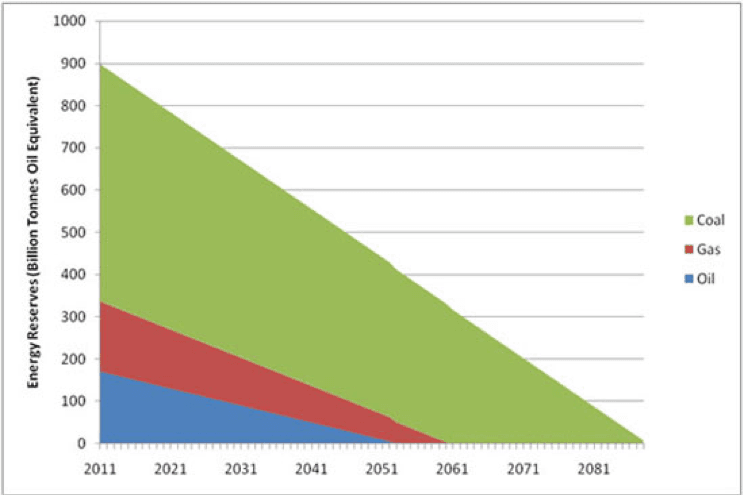
This graph indicates that if we do not make significant changes to the way we source and generate electricity, we will see the depletion of fossil fuels in our lifetime.
There are a number of renewable energy sources we can use instead of burning the ozone layer with fossil fuels: solar energy (sunlight) can heat and light infrastructures; wind energy can be captured in wind turbines; movement of water creates hydroelectric power; using biomass made from plants is called bioenergy; hydrogen, once separated from its natural compound, can also be converted into energy. Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s heat and can be used to produce electric power, and tidal energy is drawn from the ocean tides, a result of the gravitational pull of the moon and sun.
3. Monopoly Control of Supply and Pricing of Energy
Electricity is the driving force of modern society. It is generated, distributed and sold by an electric utility. Most commonly, these companies are a natural monopoly in their industry. This is due to the high start up costs the company endured: setting up power plants, distribution networks and power grids; and lack of competition. This allows the company to charge higher prices and increases their market power, without necessarily offering a better quality product. This in turn has negative effects on the consumer, with few alternative options available.
This is leading consumers and companies to think about seeking alternative methods of sourcing electricity. Several panels around the world are starting to discuss innovations within this sector of the industry, like how technology can come into play in the distribution and creation of other sources of renewable energy. By embracing these new ways of creating and distributing electricity, we can take the power out of the big corporate’s hands and into the hands of the consumer.
4. Irreversible Environmental Damages
Our planet is currently facing a number of environmental problems. Global warming, acid rain, air pollution, urban sprawl, waste disposal, ozone layer depletion, water pollution and climate change are all consequences of our negligence and ignorance. And the most significant contribution to the deterioration of our planet: fossil fuels. Every point of the fossil fuel supply chain is causing damage; from extraction processes, transportation from the mine or well, the burning process to the toxic waste byproducts.
The following environmental damages are directly linked to the electric power industry:
- Air pollution – contamination is created by the burning of fossil fuels, discharging different gasses and poisons into the air
- Land pollution – the degradation of the earth’s surface is caused by human activities like mining and industrial activities. These have harmful effects on human health.
- Climate change and global warming – burning fossil fuels release greenhouse gases which have a direct impact on atmosphere. This causes environmental changes like melting of polar ice, change in seasons, new sicknesses, and temperature increases.
- Natural resource depletion – non-renewable resources are limited, burning them at the alarming rate that we are is leading to global warming and increased sea levels
- Acid rain – occurring when chemicals released into the environment mix with water molecules and rain down. This is prevalent in most of eastern Europe (from Poland to Scandinavia), the eastern third of USA and the southeastern region of China.
5. Lack of Government Support and Funding for Renewable Energy
We’ve discussed all the reasons why we need to move to more sustainable energy sources, so why aren’t we implementing them? Studies indicate that most countries have an enormous potential for renewable energy production, so why no shift? Slow development of renewable energy implementation can come down to a number of reasons: inadequate funds, lack of infrastructure, lack of technological advances and underprivileged energy policies. Unfortunately, a country’s economic status determines the level of renewable energy adoption.
Developing countries lack initial capital and the availability of incentive and subsidies from government, the funding to finance infrastructural developments required to set up and develop renewable energy plants. India, for example, is rich in both renewable and conventional energy resources, but continues to use coal as their dominant source of electricity. As it’s abundantly available and relatively low cost, there is no priority from government to pursue a more eco-friendly route. This is also contributed by the lack of complete energy policy declarations from government (several renewable energy technologies remain in advancement phase).
Conclusion
Electricity and gas are part of our everyday life, but the way we consume it hasn’t changed in the past 20 years, and the price has increased astronomically. Here to disrupt the energy supplier market, Energy One is already serving thousands of customers since 2017. Energy One has built the technological foundation to manage transactions in the energy sector. Merging blockchain-based products and services with a new way of consuming and sharing energy, a sustainable future is closer than we think.
Blockchain is enabling us to move from an ownership economy to a shared economy, making it possible for us to share resources. ENERGY One is embracing this technology, using it to make significant efforts to save the environment, as well as save money for the individual. By implementing sustainable energy systems within cities, individuals will be able to trade sustainable energy on a peer-to-peer level.
By embracing this new technology we not only save money as an individual, we also make significant efforts to save the environment.